stainless steel plate high temperature high creep resistant 12x24|high temperature stainless steel requirements : purchaser Once the design parameters have been established, the engineer may then evaluate the materials that appear to be capable of meeting the design strength requirements. For . See more Resultado da 17 de abr. de 2022 · PequiPodcast - Isadora Leite - Conteúdo adulto e seus tabus. PEQUI PODCAST. 2.37K subscribers. Subscribed. 77. Share. 5.2K .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Seja bem vindos ao meu close fans .. Conteúdos exclusivos , espero que goste 😏 ️ •Conteúdo sensual 🔥🔥
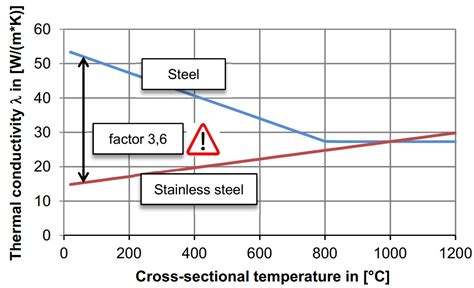
There are four design factors that engineers consider when choosing materials for service at elevated temperature. These design factors are: Service life Allowable . See moreOnce the design parameters have been established, the engineer may then evaluate the materials that appear to be capable of meeting the design strength requirements. For . See moreAnother factor to consider in designing for high-temperature service is the amount of deformation that can be permitted during the total service life. . See more
The effect of exposure of a material to media can be a very complex subject. Elevated temperatures tend to increase corrosive action, heat transfer may affect corrosivity, thermal cycling can increase metal wastage through spalling of protective scale on . See moreTherma 310S/4845 (EN 1.4951) is an austenitic heat- and creep-resisting stainless steel with excellent oxidation resistance in mildly cyclic conditions and is best employed in high temperatures up to 1050°C/1920°F. A family of creep-resistant, alumina-forming austenitic (AFA) stainless steel alloys is under development for structural use in fossil energy conversion and combustion system applications. The AFA alloys developed to .
Outokumpu high-temperature stainless steels have been specifically designed for temperatures up to 1150°C. This durability has been achieved by the addition of several significant alloying elements in the steel – ensuring superior . This expansion coefficient not only varies between steel grades, it also increases slightly with temperature. Grade 304 has a coefficient of 17.2 x 10-6 /°C over the temperature range 0 to 100°C but increases above this .
Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Caterpillar (CAT) have recently developed a new cast austenitic stainless steel, CF8C-Plus, for a wide range of high-temperature applications, including diesel exhaust components and turbine casings. The creep-rupture life of the new CF8C-Plus is over ten times greater than that of the standard cast CF8C stainless . Austenitic Stainless Steels for High Temperature Applications PHILIP J. MAZIASZ 1,2 1.—Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37831, USA. 2.—e-mail: [email protected] Austenitic stainless steels are cost-effective materials for high-temperature applications if they have the oxidation and creep resistance to withstand Heat-resistant ferritic stainless steels are widely used in many high-temperature applications such as power plants, automotive exhaust manifolds and solid oxide fuel cell interconnects due to their low price, low coefficient of thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, high thermal fatigue resistance, high creep performance and excellent .
stainless steel high temperature resistance
Therma 304H/4948 is an austenitic Core 304/4301 variant with improved high-temperature creep strength that is best employed in temperatures up to 750°C/1380°F. . is an austenitic heat- and creep-resisting stainless steel with excellent oxidation resistance in mildly cyclic conditions and is best employed in high temperatures up to 1050°C .than stainless steel type, we aim to make choosing the best product for your application easier. The Therma range stainless steels are designed for applications with service temperatures above 550 °C/1020 °F. These products give you better oxidation and high temperature corrosion resistance as well as long-term creep resistance.Due to the loading and to the temperature, these devices are submitted to creep under complex atmosphere with low oxygen partial pressure content. Unusual damages and high creep strain rates have been reported on components made of 310S Stainless Steel. Therefore, the mechanical behavior at high temperature of this alloy was investigated. Many dataAlloy 321 stainless steel plate is also advantageous for high temperature service because of its good mechanical properties. Alloy 321 stainless steel plate offers higher creep and stress rupture properties than Alloy 304 and, particularly, Alloy 304L, which might also be considered for exposures where sensitization and intergranular corrosion .
Thermo-mechanical treatments (TMT) at different rolling deformation temperatures were utilized to process a martensitic heat-resistant stainless steel 403Nb containing 12 wt pct Cr and small additions of Nb and V. Microstructures and mechanical properties at room and elevated temperatures were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission . In addition to creep and fatigue, oxidation is unavoidable for alloys exposed to high-temperature oxidizing environments. For heat-resistant stainless steel, which is utilized in the production of reheater tubes, superheaters, turbine blades, and so on, breakaway oxidation is one of the primary causes of component failure at elevated temperatures [11].
During the continuous casting of 430 ferritic stainless steel, the broadening phenomenon and bulging deformation are considered a high-temperature creep. This study investigates 430 ferritic stainless steel by conducting high-temperature uniaxial creep experiments under the temperatures of 0.4-0.5 Tm and stresses of 32.5-85 MPa. After creep .
Since the first introduction of the high-entropy alloys (HEAs) [1, 2], part of characteristics of the alloys that have attracted the most attention has been solid solution strengthening due to lattice distortion and sluggish diffusion both of which would contribute to high temperature creep resistance and, therefore, high temperature structural application was . Secondary-stage creep strain/Δln t from 0.1 to 4 x 10 4 minutes for annealed austenitic stainless steel alloys 304HN, 310, and 316 plotted as a function of normalized applied stress. Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and Caterpillar have recently developed a new cast austenitic stainless steel, CF8C-Plus, for a wide range of high-temperature applications, including diesel .
High-temperature processes induce creep and corrosion, primarily resulting in failure of thin-walled pressure vessels. Investigating alloy creep behavior in these vessels is crucial due to its often undetected nature, leading to sudden and costly failures, posing irreversible risks to health and the environment. This study investigates the creep behavior of . An austenitic stainless steel displaying high temperature oxidation and creep resistance has a composition that includes in weight percent 15 to 21 Ni, 10 to 15 Cr, 2 to 3.5 Al, 0.1 to 1 Nb, and 0.05 to 0.15 C, and that is free of or has very low levels of N, Ti and V.
The first three alloys are traditional stainless steels with a relatively low Ni content (approximately 10–12 wt% Ni), while the NF709 alloy is a state-of-the-art creep-resistant stainless steel containing 25 wt% levels of Ni, and alloy 617 is a high-cost Ni-based superalloy. It is clear that the AFA-0.5Nb0.08C alloy exhibited creep .Selecting the right stainless steel or high temperature alloy for a job presents no problem if the fastener manufacturer meets required specifications. . CarTech 718 has exceptionally high yield, tensile and creep-rupture properties up to 1300°F (704°C). It has been used typically for high temperature bolts and fasteners in jet aircraft .
stainless steel high temperature
Creep behavior of AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel as one of the most fundamental materials utilized in high temperature operating conditions due to their good high-temperature mechanical . Semantic Scholar extracted view of "Precipitate characteristics and their effects on the high-temperature creep resistance of alumina-forming austenitic stainless steels" by D. Zhou et al. . stainless steel is reviewed in this paper. As a new type of heat-resistant steel, AFA steel forms an alumina protective scale instead of chromia in . A family of inexpensive, Al2O3-forming, high-creep strength austenitic stainless steels has been developed. The alloys are based on Fe-20Ni-14Cr-2.5Al weight percent, with strengthening achieved .• Creep and high temperature failure • Creep testing • Factors affecting creep • Stress rupture life time behaviour • Creep mechanisms •Example • Materials for high creep resistance-Refractory metals-Superalloys Dr. M. Medraj iversity MSE 521 Lecture 14/2 • Materials are often placed in service at elevated temperatures and static
Among the different types of steel, stainless steel shines in its impressive heat-resistant properties, especially the high-grade alloys. These alloys, such as Type 310 and Type 316, are renowned for their superior heat resistance, allowing them to withstand temperatures above 1000 degrees Celsius without sacrificing strength or corrosion . This paper reports high-temperature properties of stainless steel for structural use in comparison with conventional carbon steels. . hardening of stress-stain curves at high temperatures after the strain surpasses the elastic limit and thereby the fire resistance of stainless steel frames is considered to be excellent. . “Primary creep . Because of its excellent creep and corrosion resistance at high temperatures, Su-per304H steel is increasingly used for the major components in power plants, aero-engines, and process plants .

tearing test download
tearing test for fabric
WEBBem-vindo ao TUFOS - Mega Portal Adulto. Com conteúdo 100% original e exclusivo, o TUFOS - Mega Portal Adulto traz para você os melhores quadrinhos, desenhos animados e vídeos adultos da !
stainless steel plate high temperature high creep resistant 12x24|high temperature stainless steel requirements